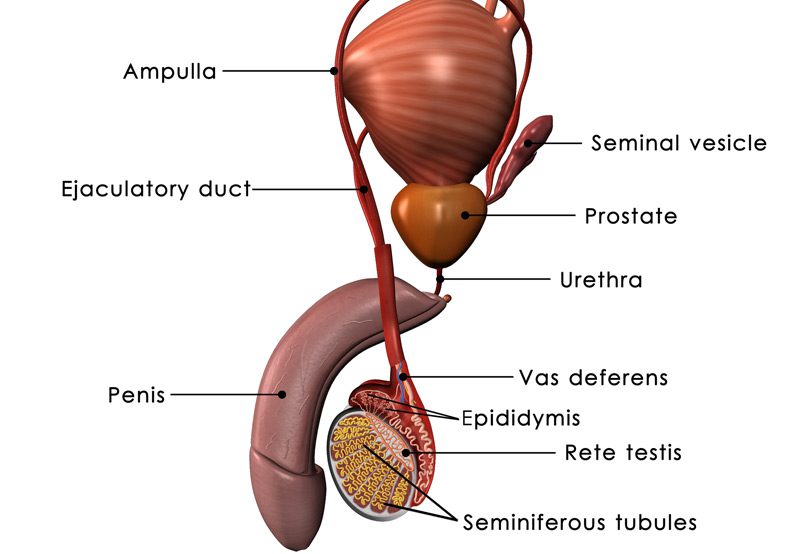
Ejaculatory disorders refer to conditions that affect the process of ejaculation, which may include:
- Premature ejaculation (ejaculating too early, often before or shortly after penetration)
- Delayed ejaculation (difficulty achieving ejaculation)
- Anejaculation (the inability to ejaculate)
- Retrograde ejaculation (semen moves backward into the bladder instead of forward through the urethra)
These conditions can cause distress, frustration, and strain on relationships, impacting both emotional well-being and sexual satisfaction.
Causes of Ejaculatory Disorders
Ejaculatory disorders can be caused by a range of physical, psychological, and lifestyle factors, including:
- Physical Characteristics: In the case of retrograde ejaculation, the opening of the bladder might not close properly.
- Psychological Factors: Anxiety, depression, performance stress, relationship problems, and past trauma can interfere with ejaculation control and function.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to ejaculatory dysfunction.
- Surgical Procedures: Prostate surgery or other pelvic surgeries may damage the nerves or structures involved in ejaculation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can contribute to ejaculatory problems due to their negative effects on blood flow and overall health.

Diagnosis
Diagnosing ejaculatory disorders typically involves:
- Medical History: Reviewing sexual history, health conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors that may be contributing to the disorder.
- Physical Exam: A thorough physical examination to check for any physical causes, such as prostate issues, nerve damage, or hormonal imbalances.
- Blood Tests: Hormonal tests to assess testosterone levels, thyroid function, and other factors that may be contributing to the disorder.
- Urine Tests: Sperm in the urine can indicate retrograde ejaculation.
Treatment Options
Treatment for ejaculatory disorders depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Medications: Stopping medications that are currently contributing to ejaculation disorders may help.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Commonly used for premature ejaculation to help delay ejaculation.
- Testosterone Therapy: Used when low testosterone levels are contributing to ejaculatory issues.
- Alprostadil: For anejaculation or other severe disorders, injections can help stimulate ejaculation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and improving diet and exercise can enhance overall sexual function and help improve ejaculatory disorders.
- Surgery: In rare cases, surgical options may be considered to correct anatomical issues, such as blocked seminal ducts or damage to the prostate.
Next Steps
Ejaculatory disorders are manageable, and finding the right solution requires identifying the root cause. Consulting with a healthcare provider can lead to a tailored treatment plan that addresses both physical and psychological aspects, improving sexual satisfaction and overall well-being.
